Cytopathology
Researching Cancer, Microscopic Analysis and Techniques
Cytopathology is probably one of, if not the most important, areas of study in the scientific community, as it observes and analyzes infected and infectious cells.
Cells are everywhere in the body and they play a large role in everything that occurs, from digestion to respiration to distribution of nutrients.
If the cells in the body acquire an infection, particularly in cases where the disease spreads or takes over, as in autoimmune diseases or cancers, the individual no longer has the ability to properly function.
It is for this reason that the study of cells is so significant and it explains the need for many analytical tools and techniques.
Cancer Cytopathology
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States and the sixth throughout the entire world, largely because the citizens of impoverished countries never live long enough to develop such an illness, as they die from basic sicknesses like diarrhea and respiratory infections.
The point is that cancer, which occurs on the cellular level, is a serious killer with regard to human life, a fact that causes it to make up the highest percentage of scientific cases in the field of cytopathology.
Since cells are everywhere, cancer can start in any location in the body and if malignant, spread to another part of the human form, which is why studying diseased or infectious cells is so vital to human survival.
Cytopathologists study many different types of cancer, but one of the most common specimens analyzed comes from a PAP smear; a technique that involves swabbing the inside of a woman’s cervix to determine whether or not she has cervical cancer.
Most medical professionals feel this is one of the most successful methods in diagnosing cancer, as estimates suggest it reduced deaths from this type of cellular disease by 70 percent.
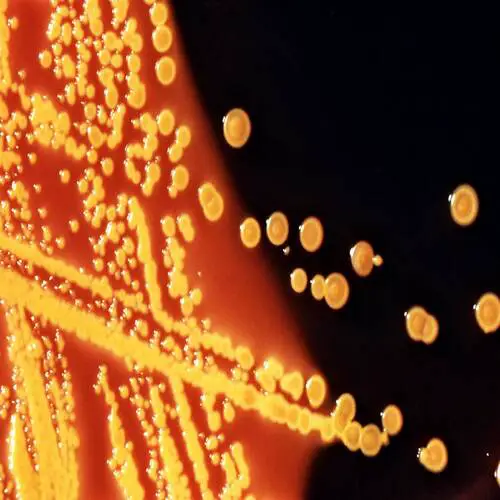
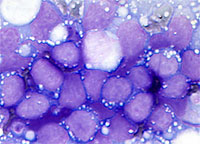
Image of Burkitt Lymphoma - from cytopathology.standford.edu
Microscopic Analysis
Cytopathology usually starts with observations made under a microscope, as a researcher has to know what they are looking at before they can test it.
When analyzing a cell under a microscope, cytopathologists have some options, as they may use a traditional, virtual through digital image capture or an electron microscope, as well as a combination of the three.
The virtual microscope is fairly new and produces accurate and insightful results. Software is required that allows for easy navigation through virtual slides, a good computer network connection is imperative and to avoid unclear images there needs to be a wide focal range.
To use the virtual/digital microscope in cytopathology, one must first create a glass slide of the specimen to protect it from contamination or damage. Once the researcher has the glass slide, they may proceed to scan it and then view the image from every angle at a variety of magnifications on a large computer screen, provided they have the appropriate scanner and software system.
A cytopathologists may use the electron microscope in place of or in conjunction with other types of microscopes, as the high-quality image produced from this device can pick up different material or simply confirm findings.
Researchers often use this microscope if they want to clarify the image to determine subtle differences in cells, like when trying to confirm whether the sample shows mesothelioma or adenocarcinoma.
Fine Needle Aspiration
Fine Needle Aspiration, or FNA, is a technique frequently used in cytopathology, as it is the collection method of choice for specific parts of the body, particularly in the neck and oral regions.
Simply put, Fine Needle Aspiration is a technique used to perform a biopsy, a typically minor procedure that involves the collection of a tissue sample large enough to undergo lab analysis. If the area in question is in the breast region, the specimen collection occurs using a second type of aspiration known as core biopsy, which uses a larger needle or in some cases, vacuum tools.
In addition to using Fine Needle Aspiration, cytopathologists are often responsible for radiological and endoscopic aspirations as a means of controlling the preparation and handling of the specimen, thus providing a more adequate sample for testing.
The purpose of this area of cytopathology is not only to obtain a correct diagnosis but also to determine treatment options based on the severity of the individual case.
Exfoliative Cytopathology
Exfoliative Cytopathology does not pertain to a single collection method or to just one type of specimen but rather, it includes a variety of samples from membranes to fluids to washings. Each sample goes through the process of staining prior to becoming a slide and then it undergoes microscopic review so that the researcher can conduct an analysis and record the findings.
The reason for its use is that it provides superior results in comparison to other collection methods, including the PAP smear, which is subject to false negatives, and Fine Needle Aspiration.
Purpose of Analysis
The techniques and tools used to study cell disease, while different, all serve the same purpose, which it to test a specimen.
The reason a researcher performs an analysis is because a doctor wants to screen a patient as a preventive method or diagnose someone who is symptomatic of a disease.
A screening may occur as part of an annual check-up, such as a PAP smear, due to poor lifestyle habits, like smoking and a high-fat diet or as a result of genetics, in which case a blood-relative had a disease, so the patient is at risk of acquiring the same illness. Since this is a preventive method, the patient does not have to show symptoms for the physician to order the tests.
If a screening comes back with positive results or if a patient has symptoms of an illness, then the doctor orders a diagnostic test to determine if a particular disease is present, the type of disease it is and its present stage.
Once the doctor receives the analysis, they can proceed to order further tests or determine available treatment options.
Cytopathology is a vital field to the progression of human health and though it encompasses the study of all diseased cells, a main focus is on cancer because this killer is responsible for 25 percent of the cases reviewed by cytopathologists.
A small segment of this field thoroughly studies other cell diseases but all share the same hope that, through technological advancements and progression, they will make discoveries leading to new treatments and life-saving cures.
As mentioned, diagnosis through microscopic analysis can be done digitally. Read more on digital pathology.
Check out cells used in research such as those of the Zebrafish and HeLa cells.
Read about Histopathology and Cytochemistry.
MicroscopeMaster loves the study of cells, continue on to read about Cell Theory, Prokaryotes or Eukaryotes as well as Cell Division.
More interesting reading: A MicroscopeMaster review of the book Molecular Biology of the Cell 5th edition.
Return from Cytopathology to Microscope Applications
Return from Cytopathology to Microscopy Research Home
Find out how to advertise on MicroscopeMaster!