Microscope Parts and Functions
With Labeled Diagram and Functions
How does a Compound Microscope Work?
Before exploring microscope parts and functions, you should probably understand that the compound light microscope is more complicated than just a microscope with more than one lens.
First, the purpose of a microscope is to magnify a small object or to magnify the fine details of a larger object in order to examine minute specimens that cannot be seen by the naked eye.
Here are the important compound microscope parts...
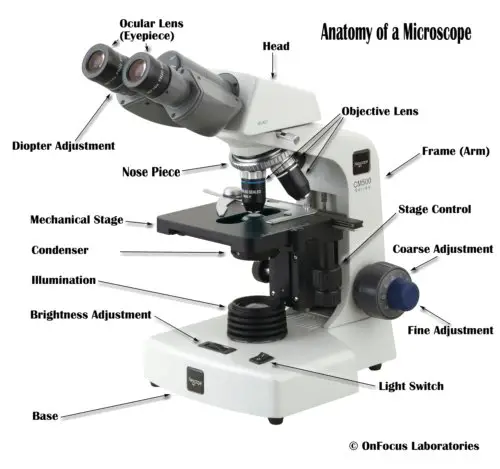

Eyepiece: The lens the viewer looks through to see the specimen. The eyepiece usually contains a 10X or 15X power lens.
Diopter Adjustment: Useful as a means to change focus on one eyepiece so as to correct for any difference in vision between your two eyes.
Body tube (Head): The body tube connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses.
Arm: The arm connects the body tube to the base of the microscope.
Coarse adjustment: Brings the specimen into general focus.
Fine adjustment: Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the specimen.
Nosepiece: A rotating turret that houses the objective lenses. The viewer spins the nosepiece to select different objective lenses.
Objective lenses: One of the most important parts of a compound microscope, as they are the lenses closest to the specimen.
A standard microscope has three, four, or five objective lenses that range in power from 4X to 100X. When focusing the microscope, be careful that the objective lens doesn’t touch the slide, as it could break the slide and destroy the specimen.
Specimen or slide: The specimen is the object being examined. Most specimens are mounted on slides, flat rectangles of thin glass.
The specimen is placed on the glass and a cover slip is placed over the specimen. This allows the slide to be easily inserted or removed from the microscope. It also allows the specimen to be labeled, transported, and stored without damage.
Stage: The flat platform where the slide is placed.
Stage clips: Metal clips that hold the slide in place.
Stage height adjustment (Stage Control): These knobs move the stage left and right or up and down.
Aperture: The hole in the middle of the stage that allows light from the illuminator to reach the specimen.
On/off switch: This switch on the base of the microscope turns the illuminator off and on.
Illumination: The light source for a microscope. Older microscopes used mirrors to reflect light from an external source up through the bottom of the stage; however, most microscopes now use a low-voltage bulb.
Iris diaphragm: Adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen.
Condenser: Gathers and focuses light from the illuminator onto the specimen being viewed.
Base: The base supports the microscope and it’s where illuminator is located.
How Does a Compound Microscope Work?
All of the parts of a microscope work together - The light from the illuminator passes through the aperture, through the slide, and through the objective lens, where the image of the specimen is magnified.
The then magnified image continues up through the body tube of the microscope to the eyepiece, which further magnifies the image the viewer then sees.
Learning to use and adjust your compound microscope is the next important step.
It's also imperative to know and understand the best practices of cleaning your microscope.
The microscope parts work together in hospitals and in forensic labs, for scientists and students, bacteriologists and biologists so that they may view bacteria, plant and animal cells and tissues, and various microorganisms the world over.
Compound microscopes have furthered medical research, helped to solve crimes, and they have repeatedly proven invaluable in unlocking the secrets of the microscopic world.
Check out MicroscopeMaster’s online help:
Basics of a Compound Microscope
Diagram/Parts/Functions of a Compound Microscope
Beginner Microscope Experiments
Microscope Slides Preparations-Styles and Techniques
Prepared Microscope Slides - Benefits and Recommendations
See also: Dissecting Stereo Microscope Parts and Functions
Stereo Microscope Vs Compound Microscope
Check out this Microscope Quiz to test your knowledge
Interesting info here on Basic Microscope Ergonomics
Return from Parts of a Compound Microscope to Compound Light Microscope
Return from Parts of a Compound Microscope to Best Microscope Home
Find out how to advertise on MicroscopeMaster!